
Introduction to Exponential Organizations (ExO)
Exponential Organizations are transforming industries by harnessing disruptive technologies and agile methodologies to grow up to ten times faster than traditional businesses, with an updated focus on sustainability and leveraging global networks to drive innovation and impact.
In a world that is rapidly accelerating and dominated by technology, the concept of Exponential Organizations (ExO) has emerged as a revolutionary framework for understanding how certain companies achieve growth and impact at a much faster pace than their traditional competitors. An exponential organization leverages disruptive technologies and methodologies to outperform traditional companies, growing up to ten times faster.
The term was popularized in 2014 by Salim Ismail, an entrepreneur and strategist, in his book Exponential Organizations, which laid out the theoretical framework behind these organizations. By combining emerging technologies, decentralized networks, and a transformative purpose, these organizations have reshaped the global market, challenging traditional business models and opening new frontiers of innovation. Today, as we move toward an even more digital economy, understanding and adopting the ExO model is not just relevant but essential for organizations to remain competitive.
In this article, we will explore the core principles of the ExO concept from its original version and analyze the updates introduced in version 2, which reflect the evolution of the model in response to the new challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
The Fundamentals of ExO – Version 1
In the first version of the book, Salim Ismail describes how Exponential Organizations (ExO) are capable of achieving disproportionate growth by focusing on emerging technologies and agile structures. These organizations leverage the power of data, digital platforms, and networks to reach levels of efficiency and scalability that traditional organizations cannot match. The key to this kind of exponential growth lies in what Ismail calls the 10 attributes of ExO, which are divided into two categories: SCALE and IDEAS.
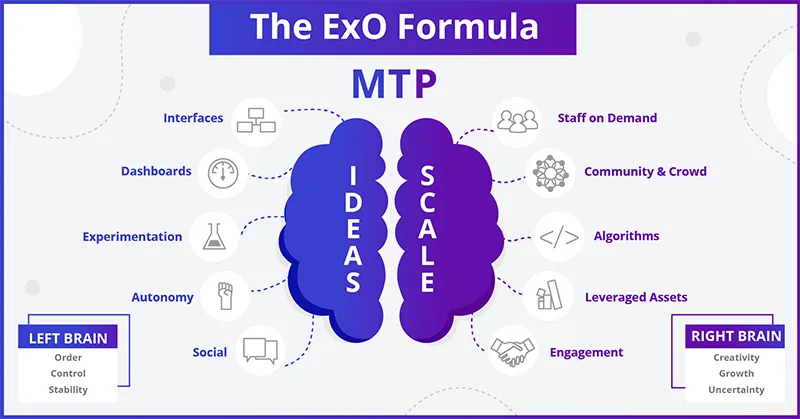
Massive Transformative Purpose (MTP): This is the essence that drives an ExO. It’s not just a traditional mission statement, but an ambitious vision that seeks to impact millions of people and solve a significant problem in the world. Clear examples include Google, whose MTP is "to organize the world’s information," or Tesla, whose purpose is "to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy." The MTP defines the organization's direction and keeps it aligned with exponential growth.
SCALE Attributes:
Staff on Demand: Instead of relying on a traditional workforce, ExOs draw on external, flexible collaborators as needed.
Community and Crowd: They leverage the collective intelligence of large communities to innovate, create, and solve problems.
Artificial Intelligence and Algorithms: They implement algorithms to automate processes and optimize operations in real-time.
Leveraged and Shared Assets: They don’t own traditional physical assets but rent or share them, as is the case with Airbnb.
Engagement: They foster participation and engagement from users, utilizing digital platforms to maintain continuous and fluid relationships.
IDEAS Attributes:
Interfaces: They create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces that allow both employees and users to interact efficiently with technological platforms.
Dashboards: They use real-time dashboards to measure performance and make data-driven decisions.
Experimentation: Constantly running experiments rather than rigid plans, adopting an agile, iterative mindset.
Autonomy: Their teams work independently, making agile decisions without relying on heavy bureaucracy.
Social Technologies: They integrate social networks as a central tool for communication and collaboration.
These attributes, working in tandem, enable organizations to operate with agility, efficiency, and adaptability, allowing them to scale quickly and remain competitive in volatile markets.
Updates and Evolution – ExO Version 2
Over the years, the global context has shifted, and exponential organizations have had to adapt to new challenges, leading to a second version of the ExO model, which introduces several adjustments and improvements. In version 2 of the book, Salim Ismail and his team revisit the original model to reflect the most recent technological innovations and new market dynamics.
One of the key changes is the integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies have expanded the potential of exponential organizations, allowing them to further automate processes and manage large-scale data to make more precise and efficient decisions.
Additionally, there has been an increased emphasis on sustainability and environmental impact, an area that has gained importance in recent years due to growing concerns over climate change and resource scarcity. Today’s ExOs must not only be efficient and agile but also environmentally responsible and socially conscious. Companies like Patagonia and Tesla are leading this transition, combining exponential growth with a strong commitment to sustainability.
Among the changes in SCALE and IDEAS attributes, there is greater diversification in the use of algorithms and automation tools, along with a deeper integration of collective intelligence through open innovation platforms. This has allowed ExOs to scale even faster, leveraging solutions and contributions from a global community.
In terms of new examples of emerging companies that have adopted the updated ExO model, standout names include OpenAI, which uses artificial intelligence to revolutionize sectors like research and automation, and Chainlink, which has implemented blockchain to transform the global financial ecosystem.
The Impact of Exponential Organizations in Today’s World

Exponential organizations have profoundly changed how industries and markets function. Sectors that were once dominated by traditional companies, such as healthcare, education, and finance, have experienced unprecedented disruption thanks to ExOs.
For example, in the healthcare industry, companies like 23andMe have revolutionized the field of genetics by offering large-scale DNA testing, while Babylon Health uses artificial intelligence to provide telemedicine services to millions of people. These organizations are challenging the traditional healthcare model and opening new avenues for personalization and efficiency.
In education, platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy have leveraged digital technologies to democratize access to education, allowing millions of students worldwide to learn at their own pace and a reduced cost.
Meanwhile, in the financial sector, the rise of FinTechs has challenged traditional banking, with companies like Revolut and Stripe leading the revolution in digital payments and financial services.
Lessons Learned from ExOs – Cases of Failure and Adaptation
While many ExOs have succeeded, not all organizations that adopt this model thrive. Some examples of failure include companies that tried to grow too quickly without a proper structure or those that failed to adapt to market demands. One such example is Jawbone, which was unable to maintain its competitive advantage in the wearable device sector.
However, there are also successful adaptation stories, such as Microsoft, which shifted from being a traditional company to adopting a more agile, cloud-focused approach, allowing it to revitalize its growth and remain relevant in the digital era.
The Future of Exponential Organizations

The future of ExOs seems promising, especially with the ongoing evolution of technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and robotics. Over the next 10 years, more industries are expected to be impacted by these types of organizations, bringing disruption to previously unexplored sectors.
ExOs will also play a crucial role in solving global challenges, such as climate change and inequality, by applying advanced technologies and disruptive business models to tackle these issues on a large scale.
Conclusion
Exponential Organizations are redefining the rules of the game in the business world. With a focus on scalability, agility, and global impact, these organizations are poised to lead the next wave of disruption. The updates in version two reflect the evolution of this model, highlighting the importance of sustainability and new technologies. In summary, organizations that adopt ExO principles will be better positioned to face future challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
References:
Ismail, Salim; Van Geest, Yuri; Malone, Michael S. Exponential Organizations: New Organizations Are Ten Times Better, Faster, and Cheaper Than Yours (and What to Do About It)
Ismail, Salim; Malone, Michael S.; Diamandis, Peter H. Exponential Organizations 2.0: The New Playbook for 10x Growth and Impact
ExO Insight Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.








